Clinical Trials and Research
Sensitive Assay for Mosaicism (SAM)
What is mosaicism?Mosaicism is a condition where individuals have cells with different profiles. Mosaicism can be difficult to detect with standard genetic tests particularly if mutated cells are few.
About the Sensitive Assay for Mosaicism (SAM):At Columbia University we developed SAM to enhance our ability to identify genetic variants.
Our assay is designed to help:
- Families with a de novo mutation: If you have a previous child or pregnancy affected with a genetic variant that is not present in the parents, we analyze maternal and paternal saliva samples and paternal sperm samples to search for the specific variant.
- Fathers with a mosaic genetic condition:By assessing the mutation load in a man's sperm, families can choose the best reproductive option for their family.
Results: The results of SAM can be one of the following -
- Variant not detected in any of the samples analyzed
- Variant detected only in sperm cells but negative in other samples
- Variant detected in sperm cells and other tissues
Benefits:SAM offers personalized insights into the likelihood of genetic conditions being passed on to future generations. Personalized risk assessment with SAM can help families choose the best reproductive path for their family.
Contact us:If you have a previous child or pregnancy with a de novo mutation or a man with known mosaicism, please contact us to determine your eligibility for SAM.
PGT-M for Mitochondrial DNA Disorders (IRB AAAU8240)
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) cause rare maternally inherited conditions. The levels of mutated and normal mitochondrial DNA can vary in the eggs, the embryos, and the children of a carrier mom. The percentage of mutated mtDNA present is referred to as “mutation load”. A higher mutation load is associated with a higher risk of having a symptomatic mitochondrial disease.
Preimplantation genetic testing for mtDNA disorders (PGT-M) can be utilized to reduce the risk of mtDNA disease. Application of PGT to these conditions is investigational and requires a multi-disciplinary approach. There are less than 100 PGT-M cases for mtDNA reported worldwide, indicating a need for more information on how PGT-M might be utilized for mtDNA conditions. Our study aims to better understand the mtDNA mutation load throughout the eggs, embryo biopsy, fetus, and child.
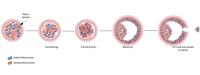
Eggs and sperm from the couple are combined in our lab and the resulting embryos are tested for the mtDNA mutation load. (Figure drawn by Leah DiBianco).
Participating in the study involves pursuing IVF and prenatal diagnostic testing. IVF involves combing eggs and sperm from the couple in our fertility clinic to create embryos. The resulting embryos are tested for the mtDNA disorder the woman carries.
If you are a female carrier of a mitochondrial DNA mutation and interested in participating in our IRB-approved study, please contact us to determine your eligibility. We are only accepting patients who can travel to New York City for their consults, treatment, and follow up. After eligibility review, you will meet with our multidisciplinary team before starting the invitro fertilization (IVF) process.
